Principles of modern chemistry 8th edition – Introducing the Principles of Modern Chemistry, 8th Edition, a comprehensive guide to the fundamental concepts and applications of chemistry. This updated edition offers a captivating exploration of the atomic structure, chemical bonding, reactions, solutions, gases, acids, bases, salts, and organic chemistry, empowering students with a thorough understanding of the field.
Through a blend of clear explanations, engaging examples, and thought-provoking exercises, this text unravels the intricacies of modern chemistry, fostering a deep appreciation for its significance in shaping our world.
Introduction to Modern Chemistry
Modern chemistry is the study of the composition, structure, properties, and change of matter. It is a vast and diverse field that encompasses a wide range of topics, from the smallest subatomic particles to the largest molecules and materials. Modern chemistry has its roots in the ancient practice of alchemy, but it has undergone a profound transformation over the centuries, thanks to the development of new experimental techniques and theoretical models.
One of the most important developments in modern chemistry was the discovery of the periodic table by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. The periodic table organizes the elements in a way that highlights their similarities and differences, and it has been a powerful tool for understanding the chemical properties of elements.
Another important development in modern chemistry was the development of quantum mechanics in the early 20th century. Quantum mechanics provides a theoretical framework for understanding the behavior of atoms and molecules, and it has led to a deeper understanding of the chemical bond.
Modern chemistry is a dynamic and rapidly evolving field. New discoveries are being made all the time, and our understanding of the chemical world is constantly expanding. Modern chemistry has had a profound impact on our lives, and it continues to play a vital role in the development of new technologies and materials.
Atomic Structure and Properties
An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the chemical properties of an element. Atoms are composed of a nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons, and electrons, which orbit the nucleus.
The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number, which is unique for each element. The number of neutrons in an atom determines its mass number, which is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons.
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The periodic table is a powerful tool for understanding the chemical properties of elements and predicting the behavior of new elements.
The properties of elements are determined by their atomic structure. For example, the number of valence electrons in an atom determines its chemical reactivity. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, and they are the electrons that participate in chemical reactions.
Chemical Bonding

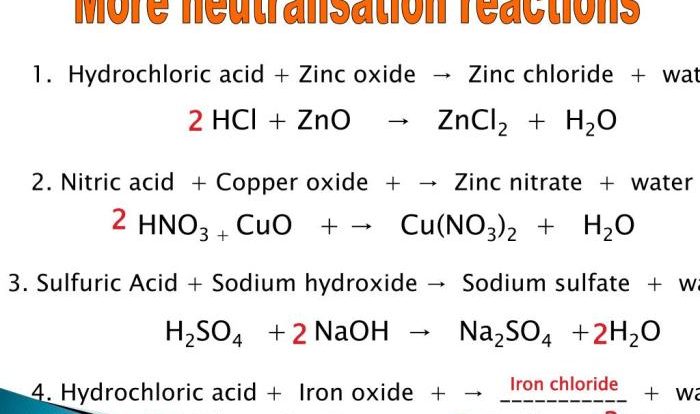
A chemical bond is a force that holds atoms together to form molecules and compounds. There are three main types of chemical bonds: ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds.
Ionic bonds are formed between atoms that have opposite electrical charges. For example, sodium (Na) has one valence electron, which it is willing to give up. Chlorine (Cl) has seven valence electrons, and it needs one more electron to complete its valence shell.
When sodium and chlorine atoms come together, the sodium atom gives up its valence electron to the chlorine atom, forming an ionic bond.
Covalent bonds are formed between atoms that share valence electrons. For example, hydrogen (H) has one valence electron, and it needs one more electron to complete its valence shell. When two hydrogen atoms come together, they share their valence electrons, forming a covalent bond.
Metallic bonds are formed between metal atoms. Metal atoms have a low ionization energy, which means that they are willing to give up their valence electrons. When metal atoms come together, they share their valence electrons, forming a metallic bond.
Commonly Asked Questions: Principles Of Modern Chemistry 8th Edition
What is the key focus of the Principles of Modern Chemistry, 8th Edition?
The Principles of Modern Chemistry, 8th Edition, provides a comprehensive overview of the fundamental principles and applications of chemistry, covering topics such as atomic structure, chemical bonding, reactions, solutions, gases, acids, bases, salts, and organic chemistry.
How is the content organized in this edition?
The text is organized into eight chapters, each focusing on a specific aspect of chemistry. The chapters are further divided into sections and subsections, providing a logical flow of information and making it easy for students to navigate the material.
What are the key features of this textbook?
The Principles of Modern Chemistry, 8th Edition, offers a range of features to enhance student learning, including clear explanations, engaging examples, thought-provoking exercises, and a variety of interactive learning tools.