Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of chemistry with the chemistry: matter and change book answer key, your trusted guide to unraveling the mysteries of matter and its remarkable transformations. This comprehensive resource delves into the fundamental concepts of chemistry, empowering you to grasp the intricate workings of the物質world.
Through a series of engaging explanations, real-world examples, and insightful exercises, the chemistry: matter and change book answer key illuminates the properties of matter, the dynamics of chemical reactions, and the principles governing chemical interactions. Whether you’re a student seeking to reinforce your understanding or an educator searching for valuable teaching materials, this answer key is an indispensable tool.
Key Concepts: Chemistry: Matter And Change Book Answer Key
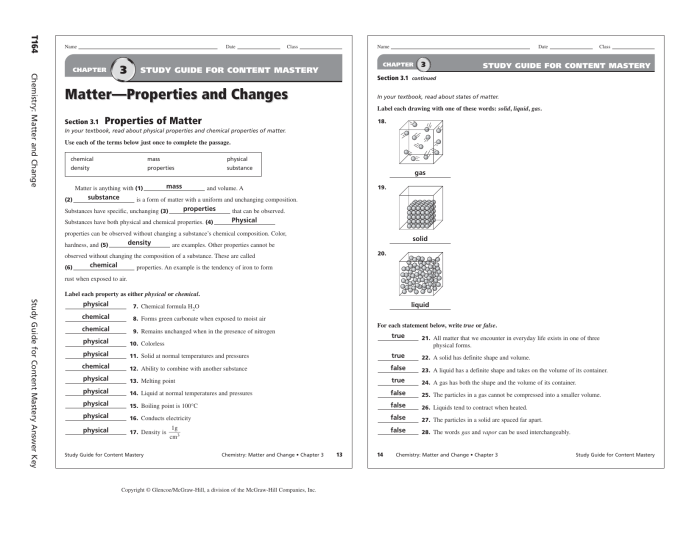
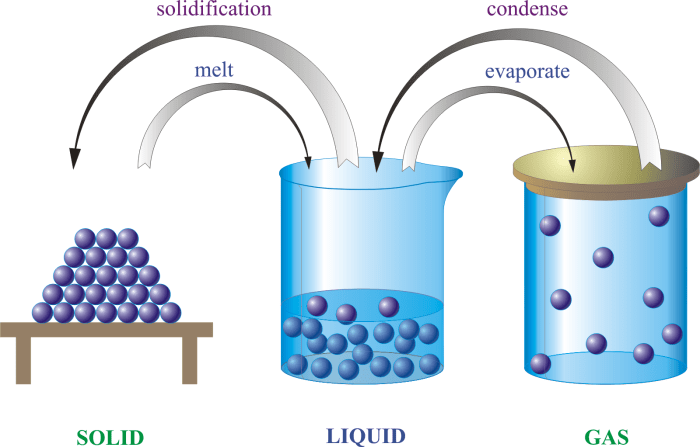
Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. It can exist in three states: solid, liquid, and gas. Chemical change is a process that changes the chemical composition of a substance. There are several types of chemical reactions, including synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, and combustion reactions.
The properties of different states of matter vary greatly. Solids have a definite shape and volume, liquids have a definite volume but no definite shape, and gases have no definite shape or volume.
Chemical Reactions
- Synthesis reactions: Two or more substances combine to form a single product.
- Decomposition reactions: A single substance breaks down into two or more products.
- Single displacement reactions: One element replaces another element in a compound.
- Double displacement reactions: Two compounds exchange ions to form two new compounds.
- Combustion reactions: A substance reacts with oxygen to produce heat and light.
The rate of chemical reactions can be affected by several factors, including temperature, concentration, and the presence of a catalyst.
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is the study of the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. Mole ratios are used to calculate the amount of reactants and products involved in a reaction. The limiting reactant is the reactant that is completely consumed in a reaction, limiting the amount of product that can be formed.
Solutions
Solutions are homogeneous mixtures of two or more substances. The solute is the substance that is dissolved in the solvent. The concentration of a solution is a measure of the amount of solute in a given amount of solvent.
- Types of solutions: Unsaturated, saturated, and supersaturated
Acids and Bases
Acids are substances that donate protons (H+ ions), while bases are substances that accept protons. According to the Brønsted-Lowry theory, acids are proton donors and bases are proton acceptors. The pH of a solution is a measure of its acidity or basicity.
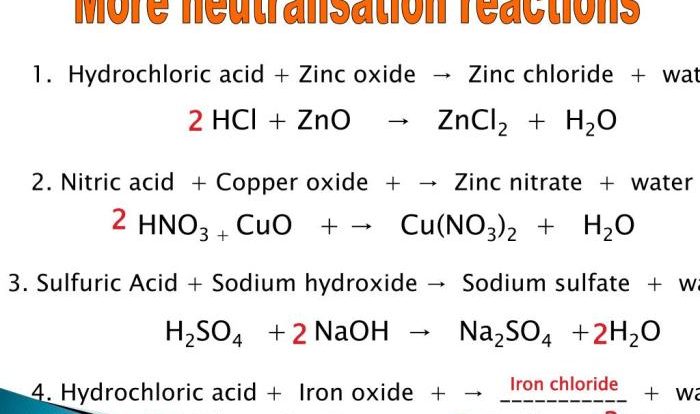
Acids and bases react with each other to form salts and water in a neutralization reaction.
Gases, Chemistry: matter and change book answer key
Gases are fluids that have no definite shape or volume. They expand to fill the container they are in. The properties of gases can be described by the gas laws, which relate pressure, volume, and temperature.
- Boyle’s Law: The pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume.
- Charles’s Law: The volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature.
FAQ Summary
What is the definition of matter?
Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.
What are the three states of matter?
The three states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas.
What is a chemical change?
A chemical change is a change in the composition of matter.