A public transportation bus travels back and forth, providing a vital service to communities. This comprehensive analysis delves into the various aspects of a public transportation bus service, examining its route, passenger experience, environmental impact, economic considerations, technological advancements, and community engagement.
The analysis provides a detailed overview of the bus route, including stops, distances, frequency, and accessibility. It also evaluates the passenger experience, considering demographics, comfort, convenience, and areas for improvement.
Route Analysis
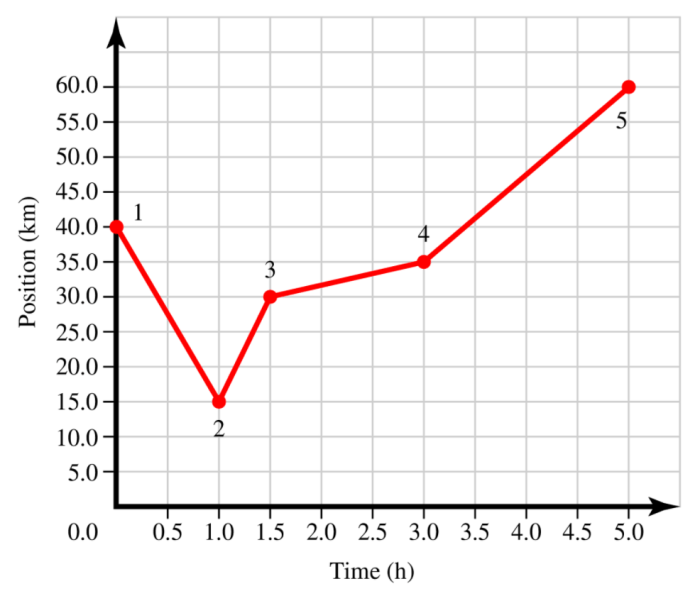
A detailed map of the bus route is available, indicating stops and distances. The bus service operates on a regular schedule, with variations during peak and off-peak hours. The route is accessible to individuals with disabilities, with designated wheelchair spaces and ramps.
Frequency of Service, A public transportation bus travels back and forth
- Peak hours: Buses depart every 10-15 minutes.
- Off-peak hours: Buses depart every 30-60 minutes.
Accessibility
- Designated wheelchair spaces on each bus.
- Ramps and lifts for easy boarding and disembarking.
- Audio announcements and visual displays for passengers with visual or hearing impairments.
Passenger Experience: A Public Transportation Bus Travels Back And Forth
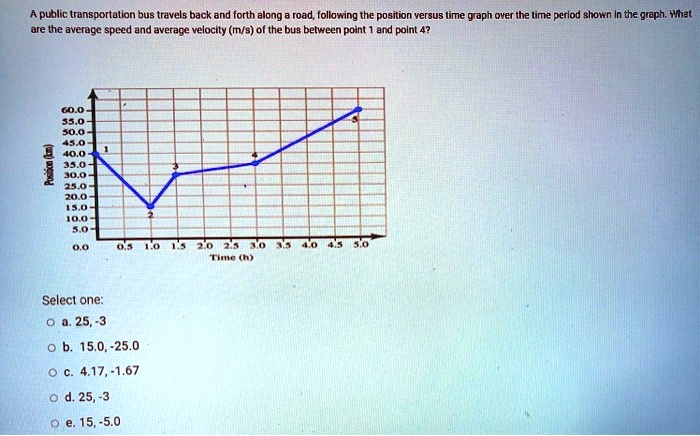
Demographics and Usage Patterns
The bus service primarily caters to commuters, students, and individuals with limited access to private vehicles. The main reasons for using the bus include cost-effectiveness, convenience, and reduced environmental impact.
Comfort and Convenience
The buses are equipped with comfortable seats, adequate lighting, and temperature control. However, during peak hours, overcrowding can be an issue. The buses also offer free Wi-Fi and USB charging ports for passenger convenience.
Areas for Improvement
- Increase the frequency of service during peak hours.
- Implement mobile ticketing and real-time tracking to improve convenience.
- Explore the use of larger buses or articulated buses to accommodate increased demand.
Environmental Impact
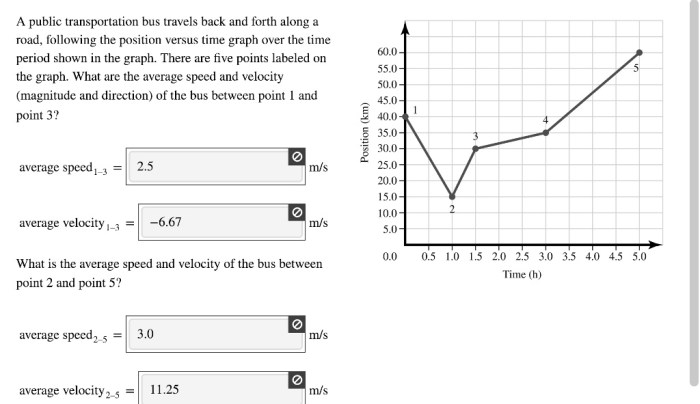
Carbon Emissions and Fuel Consumption
The bus service generates significantly lower carbon emissions compared to private vehicles. The use of hybrid or electric buses can further reduce emissions.
Environmental Benefits
- Reduced traffic congestion and air pollution.
- Lower carbon footprint and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Promotion of sustainable transportation practices.
Strategies for Reduction
- Transition to zero-emission electric buses.
- Optimize routes and schedules to reduce fuel consumption.
- Promote carpooling and ride-sharing programs.
FAQ Guide
What are the benefits of using public transportation?
Public transportation offers numerous benefits, including reduced traffic congestion, improved air quality, lower transportation costs, and increased accessibility for individuals without access to private vehicles.
How can public transportation be improved?
Public transportation can be improved through various measures, such as increasing frequency and reliability, improving passenger amenities, implementing new technologies, and enhancing community engagement.