Chapter 15 the theory of evolution worksheet answer key – Embark on a captivating journey with Chapter 15: Theory of Evolution Worksheet Answer Key, a comprehensive guide to unraveling the mysteries of life’s evolution. This worksheet provides an in-depth exploration of the fundamental principles, compelling evidence, and ongoing debates surrounding the theory of evolution, offering a deeper understanding of the processes that have shaped the diversity of life on Earth.
Through a blend of scientific inquiry and thought-provoking discussion, this worksheet delves into the historical context, key concepts, and supporting evidence for the theory of evolution. Prepare to engage with real-world examples, explore the mechanisms driving evolutionary change, and critically examine common misconceptions, fostering a comprehensive understanding of this transformative scientific theory.
1. Evolutionary Theory Overview
The theory of evolution is a scientific explanation for the diversity of life on Earth. It posits that all living organisms have descended from a common ancestor through a process of gradual change over time.
Historical Context
- Ancient Greek philosophers, such as Anaximander, proposed ideas of biological change.
- Carolus Linnaeus developed a hierarchical system for classifying organisms, which laid the foundation for modern taxonomy.
- Georges Cuvier’s work on comparative anatomy provided evidence for the unity and diversity of life.
- Jean-Baptiste Lamarck proposed the first comprehensive theory of evolution, which was later superseded by Darwin’s theory.
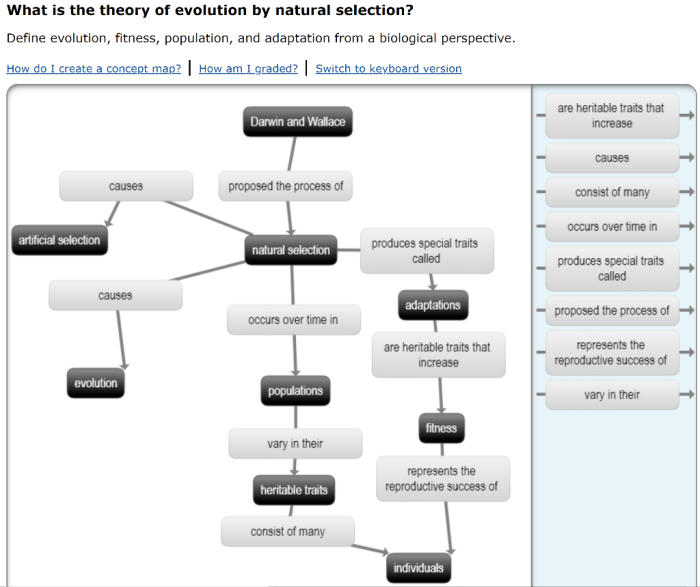
Central Tenets
- All living organisms are descended from a common ancestor.
- Evolution occurs through natural selection, a process in which individuals with advantageous traits have a higher chance of survival and reproduction.
- Over time, natural selection can lead to significant changes in populations, resulting in the formation of new species.
Role of Natural Selection
- Natural selection acts on heritable traits, which are passed down from parents to offspring.
- In any population, there is variation in traits, and some variations may be more advantageous in a given environment.
- Individuals with advantageous traits have a higher chance of surviving and reproducing, passing on their traits to their offspring.
- Over time, this process can lead to an increase in the frequency of advantageous traits in the population.
2. Evidence for Evolution: Chapter 15 The Theory Of Evolution Worksheet Answer Key
Fossil Records
Fossil records provide direct evidence of past life forms and their changes over time.
- Transitional fossils show intermediate forms between different species, supporting the idea of gradual evolution.
- The fossil record demonstrates the extinction of many species and the emergence of new ones.
Comparative Anatomy
Comparative anatomy compares the structures of different organisms to identify similarities and differences.
- Homologous structures, such as the limbs of vertebrates, indicate common ancestry.
- Vestigial structures, such as the human tailbone, provide evidence of evolutionary change.
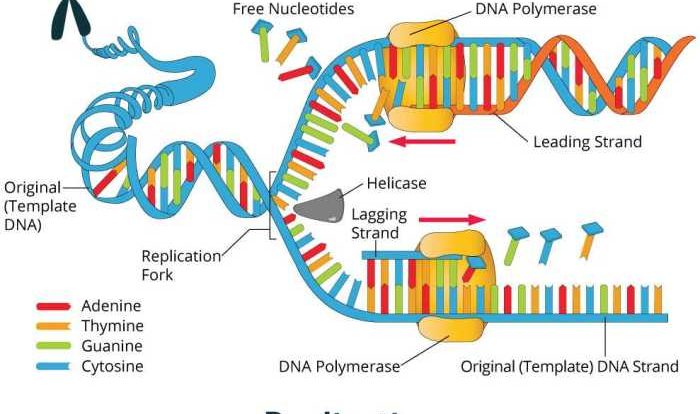
Genetics and Molecular Biology
Genetic and molecular evidence supports the theory of evolution by providing insights into the mechanisms of inheritance and genetic variation.
- DNA sequencing reveals genetic similarities between species, indicating common ancestry.
- Molecular clocks, based on the rate of DNA change, provide estimates of evolutionary time scales.
Observed Evolutionary Changes
Evolutionary changes can be observed in real-time in some species.
- Antibiotic resistance in bacteria is a well-documented example of rapid evolutionary change.
- Peppered moths provide evidence of natural selection in response to environmental changes.
3. Mechanisms of Evolution
Genetic Variation, Chapter 15 the theory of evolution worksheet answer key
Genetic variation is the raw material for evolution, providing the diversity of traits upon which natural selection can act.
- Mutations are random changes in DNA that can introduce new traits.
- Genetic recombination, such as crossing-over during meiosis, shuffles genetic material, creating new combinations of alleles.
Gene Flow
Gene flow is the transfer of genes between populations.
- Migration of individuals can introduce new alleles into a population.
- Gene flow can reduce genetic variation within populations and increase it between populations.
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift is the random change in allele frequencies due to chance events.
- Genetic drift can lead to the loss of alleles, especially in small populations.
- It can also lead to the fixation of alleles, even if they are not advantageous.
Population Bottlenecks
Population bottlenecks are events that drastically reduce the size of a population.
- Bottlenecks can lead to a loss of genetic variation and an increase in homozygosity.
- They can also increase the impact of genetic drift.
4. Evolution in Action
Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria
Antibiotic resistance is a prime example of rapid evolutionary change in response to selective pressure.
- Bacteria with mutations that confer antibiotic resistance have a higher chance of surviving and reproducing in the presence of antibiotics.
- Over time, the frequency of antibiotic-resistant bacteria increases in the population.
Peppered Moths
Peppered moths provide evidence of natural selection in action.
- During the Industrial Revolution, dark-colored moths had an advantage in polluted areas because they blended better with the soot-covered trees.
- In unpolluted areas, light-colored moths had an advantage because they were better camouflaged against the lichen-covered trees.
Implications for Human Health and the Environment
Evolution has significant implications for human health and the environment.
- Understanding evolutionary principles helps us develop strategies to combat antibiotic resistance.
- Evolutionary knowledge is essential for conserving biodiversity and mitigating the effects of climate change.
5. Misconceptions and Controversies
Common Misconceptions
- Evolution is not a theory but a fact.
- Evolution does not mean that humans descended from monkeys.
- Evolution does not imply that life is meaningless.
Role of Religion and Culture
Religious and cultural beliefs can influence perceptions of evolution.
- Some religious groups interpret their scriptures as supporting creationism rather than evolution.
- Cultural beliefs about human exceptionalism can lead to resistance to evolutionary ideas.
Evidence-Based Responses to Arguments Against Evolution
- The fossil record provides overwhelming evidence for the gradual change of species over time.
- Molecular evidence, such as DNA sequencing, supports the common ancestry of all living organisms.
- Observed evolutionary changes, such as antibiotic resistance, demonstrate the power of natural selection.
Questions Often Asked
What is the central tenet of the theory of evolution?
The central tenet of the theory of evolution is that all living organisms share a common ancestor and have undergone gradual changes over time through natural selection.
What is the role of natural selection in shaping species?
Natural selection is the driving force behind the evolution of species. It favors individuals with traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success in a given environment.
How does the fossil record provide evidence for evolution?
The fossil record provides a chronological sequence of organisms that have existed on Earth over time, demonstrating the gradual changes in species over millions of years.