Which of the following statements is true of hypoglycemia? Hypoglycemia, a condition characterized by abnormally low blood sugar levels, poses significant health risks. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and management strategies is crucial for effective prevention and treatment.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of hypoglycemia, exploring its definition, common causes, and associated symptoms. It highlights the risk factors and potential complications, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and proper management.
Definition and Causes
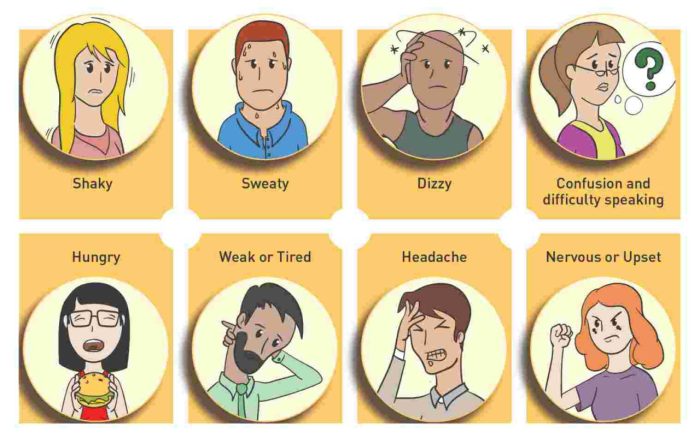

Hypoglycemia is a condition characterized by abnormally low blood sugar levels. It is defined as a blood glucose concentration below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L) in non-diabetic individuals and below 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) in diabetic individuals.
Common causes of hypoglycemia include:
- Excessive insulin secretion, such as in insulinomas or sulfonylurea overdose
- Insufficient food intake, such as in fasting or anorexia nervosa
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Certain medications, such as salicylates and beta-blockers
- Endocrine disorders, such as Addison’s disease or hypopituitarism
Symptoms and Signs
Symptoms and signs of hypoglycemia can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Mild hypoglycemia may cause:
- Shakiness
- Sweating
- Hunger
- Anxiety
- Tachycardia
Moderate hypoglycemia may lead to:
- Confusion
- Difficulty concentrating
- Blurred vision
- Headache
- Seizures
Severe hypoglycemia can cause:
- Loss of consciousness
- Coma
- Brain damage
- Death
Risk Factors and Complications

Individuals with diabetes, especially those using insulin or sulfonylureas, are at increased risk of hypoglycemia.
Other risk factors include:
- Renal impairment
- Hepatic impairment
- Elderly age
- Excessive physical activity
- Alcoholism
Untreated or severe hypoglycemia can lead to serious complications, including:
- Seizures
- Coma
- Brain damage
- Cardiovascular complications
- Death
Diagnosis and Management
Hypoglycemia is diagnosed based on symptoms and blood glucose measurements. A blood glucose level below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L) in non-diabetic individuals or below 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) in diabetic individuals is diagnostic of hypoglycemia.
Management of hypoglycemia involves:
- Immediate treatment with oral glucose or glucagon
- Identification and correction of the underlying cause
- Dietary modifications, such as frequent small meals and avoiding alcohol
- Medications, such as octreotide or diazoxide
- Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and stress management
Prevention and Education
Preventing hypoglycemia involves:
- Regular blood glucose monitoring in diabetic individuals
- Eating frequent small meals and avoiding prolonged fasting
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Carrying a source of fast-acting glucose, such as glucose tablets or gel
Patient education is crucial for effective management of hypoglycemia. Patients should be educated about:
- Symptoms and signs of hypoglycemia
- Appropriate treatment measures
- Lifestyle modifications to prevent hypoglycemia
- Importance of regular blood glucose monitoring
Query Resolution: Which Of The Following Statements Is True Of Hypoglycemia
What are the common causes of hypoglycemia?
Common causes include insulin overdose, certain medications, excessive alcohol consumption, and prolonged fasting.
What are the key symptoms of hypoglycemia?
Symptoms may include sweating, shakiness, hunger, confusion, and blurred vision.
Who is at risk of developing hypoglycemia?
Individuals with diabetes, those taking insulin or certain medications, and those with liver or kidney disease are at increased risk.
How is hypoglycemia diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a physical exam, blood tests to measure blood sugar levels, and a review of medical history.
What are the treatment options for hypoglycemia?
Treatment typically involves consuming sugary foods or drinks to raise blood sugar levels, followed by a balanced meal to prevent recurrence.